Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG): A Comprehensive Guide
In the world of AI, Large Language Models (LLMs) have shown incredible promise. However, they are not without their limitations, particularly when it comes to hallucinations—the phenomenon where a model generates information that is plausible-sounding but factually incorrect. In this blog, we’ll explore how Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) can help address these limitations, implement it effectively, and understand its architecture, benefits, and challenges.
Understanding Hallucinations in LLMs
LLMs can sometimes create outputs that sound accurate but are entirely fabricated. For example, if you ask a model about a specific historical event, it might confidently present incorrect details. This limitation can severely affect the reliability of AI applications, especially in critical fields like healthcare and finance.
Techniques to Tackle Hallucinations
To mitigate these hallucinations, several techniques can be employed, including:
- Retrieval Mechanisms: Implementing a retrieval component that fetches verified data from external sources can significantly enhance the accuracy of LLM outputs.
- Fine-Tuning: Adjusting model parameters with domain-specific data can help tailor the model’s outputs to your needs.
- User Feedback Loops: Incorporating user corrections can provide models with valuable learning opportunities.
Introduction to RAG
Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) is an innovative approach that combines the strengths of retrieval-based methods with the generative capabilities of LLMs. By leveraging a knowledge base during the generation process, RAG improves the relevance and accuracy of AI responses.
RAG Architecture
The architecture of a RAG system typically consists of:
- Retriever: This component searches a knowledge base for relevant documents or data based on a user query.
- Generator: After the retrieval step, the generative model synthesizes an answer using the retrieved information.

Recommended Architectural Framework
Adopting RAG requires a thoughtful architectural approach. The blueprint suggests a framework that seamlessly integrates the retrieval and generative components. This includes robust databases, efficient indexing mechanisms for quick data retrieval, and a generative model that can effectively utilize the retrieved data. Ensuring smooth interoperability between these components is key to harnessing the full potential of RAG.
Components required in a RAG architecture:
- Knowledge Base: Think of this as RAG’s library, filled with all sorts of information from documents, databases, or even APIs. It’s like a treasure trove of knowledge for RAG to use.
- User Query: This is where you come in. You ask a question or make a request, and RAG starts its magic.
- Retrieval Model:
- Embedding Model: This part turns the text from your question and the information in the knowledge base into numbers. It’s like translating languages, but instead, it translates words into a form that the system can understand and compare.
- Search Engine: Armed with these numerical translations, RAG then searches through its library to find the most relevant information. It’s like having a super-efficient librarian at your service.
- Generation Model:
- Large Language Model (LLM): This is where RAG gets creative. It uses advanced text generation models (think of them as super-smart writing tools) like GPT-3 to craft a response that’s both informative and easy to understand.
- Integration and Orchestration:
- Prompt Engineering: This is a bit like scriptwriting for RAG. It takes the information found and mixes it with your original question to set the scene for the LLM.
- Model Serving: This is the backstage crew, making sure RAG gets your question and sends back the right answer.
- Extra Bits:
- Monitoring and Logging: Keeps an eye on RAG to make sure it’s doing its job right.
- User Interface: This is where you interact with RAG, like in a chatbot or search engine.
A key component of the architecture is the Vector Database. It is used to store high-dimensional embeddings of text documents. Its primary role is to enable fast and efficient retrieval of information that is semantically similar to a given query. This retrieval is crucial for the RAG model to generate accurate and contextually relevant responses. The vector database ensures scalability, speed, and continuous updating of information, enhancing the overall performance of the RAG system.
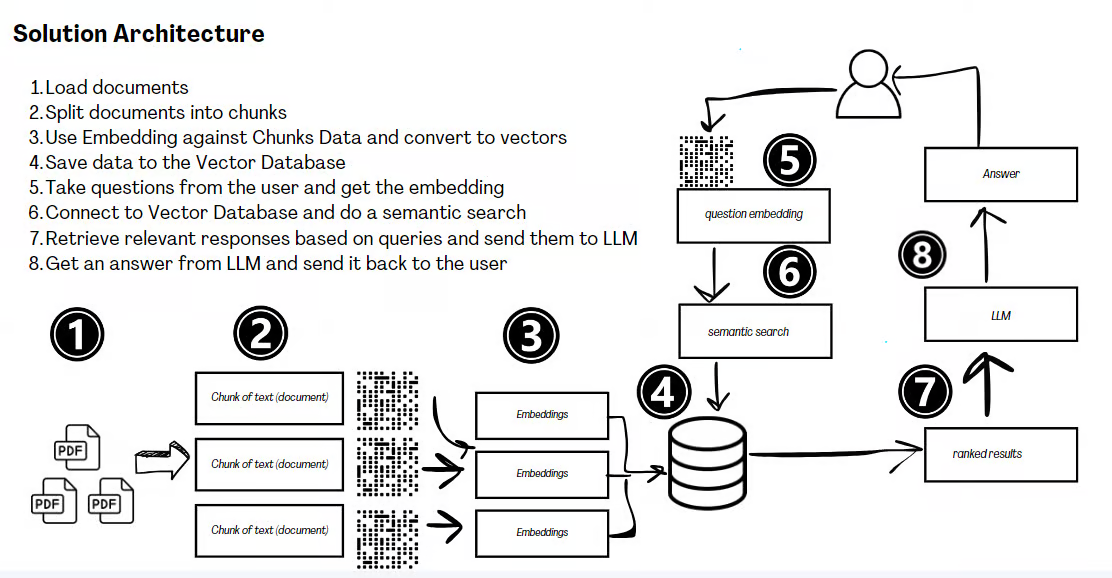 RAG Solution Architecture
RAG Solution Architecture
Benefits of RAG
-
Cost-effective Training: RAG requires less computational power and data compared to extensive fine-tuning or training LLM processes.
-
Access to Various Knowledge Sources: RAG combines internal knowledge with that from external databases, resulting in more accurate answers.
-
Enhanced Scalability: RAG can handle large datasets and intricate queries, surpassing conventional LLMs limited by their context window size.
Limitations of RAG
-
Risk of Hallucinations: RAG can still make errors if the database lacks certain information.
-
Managing Scalability: Increasing the database size can complicate quick and efficient data retrieval.
-
Potential Biases: Biases in the retrieval database can influence the responses, necessitating tools to identify and mitigate these biases.
The Grand Dilemma: RAG vs Fine-Tune
The debate in Generative AI often revolves around choosing between RAG and fine-tuning LLMs. This choice is influenced by the need for domain-specificity and the rate of data change.
I have put together a table to guide you through the decision-making process:
| Aspect | Fine-Tuning | Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) |
|---|---|---|
| Advantages | - Mitigates knowledge gaps with updated, specific data. - Cost-effective compared to full model retraining. - Suitable for training on private or specialized data. |
- Provides near-real-time data updates. - Enhances transparency with source citations. - Offers better data access control and personalization. |
| Challenges | - Struggles with frequent data updates. - Lacks clear traceability to original data sources. - Potential for inaccurate information. |
- Relies heavily on the efficiency of the search system. - Limited in context size provided to LLMs. - Possible over-reliance may curb model creativity. |
| Application | - Best for stable, less sensitive data. | - Ideal for scenarios requiring real-time data relevance and flexibility. |
Blending fine-tuning and RAG could leverage their respective strengths, using fine-tuning for stable, less sensitive data, and RAG for real-time data relevance and flexibility. This combination could offer a comprehensive solution in advanced Generative AI applications.
From my hands-on experience, it’s clear: around 60% of current use cases are swiftly embracing the RAG approach, marking a transformative shift in practical AI application.
Implementation Guide for RAG
1. Setting Up Your RAG Environment
Before diving into implementation, let’s set up a basic environment. For this guide, we’ll support both OpenAI and Ollama:
pip install langchain chromadb openai tiktoken ollama
2. Import the Necessary Components
from langchain.embeddings import OpenAIEmbeddings
from langchain.vectorstores import Chroma
from langchain.text_splitter import CharacterTextSplitter
from langchain.llms import OpenAI, Ollama
from langchain.chains import RetrievalQA
3. Set Up OpenAI API Key
To use OpenAI, ensure you have an API key set in your environment:
import os
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = "your-api-key-here"
4. Initialize Ollama Model
For Ollama, no API key is required. You can initialize the model directly:
ollama_llm = Ollama(model="llama2")
5. Preparing Your Data
One of the most crucial steps in RAG is properly preparing your data. Here’s an example of how to process a text document:
with open('your_document.txt', 'r') as file:
raw_text = file.read()
text_splitter = CharacterTextSplitter(chunk_size=1000, chunk_overlap=0)
texts = text_splitter.split_text(raw_text)
embeddings = OpenAIEmbeddings()
docsearch = Chroma.from_texts(texts, embeddings, metadatas=[{"source": str(i)} for i in range(len(texts))]).as_retriever()
6. Building Your RAG Pipeline
When building your RAG pipeline, you can now use either OpenAI or Ollama.
For OpenAI:
qa = RetrievalQA.from_chain_type(llm=OpenAI(), chain_type="stuff", retriever=docsearch)
For Ollama:
qa_ollama = RetrievalQA.from_chain_type(llm=Ollama(model="llama2"), chain_type="stuff", retriever=docsearch)
7. Optimizing Retrieval
Retrieval quality can make or break your RAG system. Here’s a technique to improve retrieval using semantic similarity:
from langchain.retrievers import TFIDFRetriever
from langchain.retrievers import EnsembleRetriever
# Create TFIDF retriever
tfidf_retriever = TFIDFRetriever.from_texts(texts)
# Create ensemble retriever
ensemble_retriever = EnsembleRetriever(
retrievers=[docsearch, tfidf_retriever],
weights=[0.5, 0.5]
)
# Use ensemble retriever in your QA chain
qa_ensemble = RetrievalQA.from_chain_type(llm=OpenAI(), chain_type="stuff", retriever=ensemble_retriever)
8. Handling Multi-Modal Data
RAG isn’t limited to text. Here’s how you might handle image data:
from langchain.document_loaders import UnstructuredImageLoader
loader = UnstructuredImageLoader("path/to/your/image.jpg")
image_document = loader.load()[0]
# Now you can include this in your text splitter and embedding process
9. Implementing Conversational Memory
For chatbot-like applications, maintaining context is crucial. Here’s how to add memory to your RAG system:
from langchain.memory import ConversationBufferMemory
from langchain.chains import ConversationalRetrievalChain
memory = ConversationBufferMemory(memory_key="chat_history", return_messages=True)
qa_chain = ConversationalRetrievalChain.from_llm(
llm=OpenAI(),
retriever=docsearch,
memory=memory
)
result = qa_chain({"question": "What's the document about?"})
print(result['answer'])
# Follow-up question
result = qa_chain({"question": "Can you elaborate on that?"})
print(result['answer'])
10. Handling Streaming Responses
For a more responsive user experience, you might want to stream the LLM’s response:
from langchain.callbacks.streaming_stdout import StreamingStdOutCallbackHandler
from langchain.llms import OpenAI
llm = OpenAI(streaming=True, callbacks=[StreamingStdOutCallbackHandler()], temperature=0)
qa_chain = RetrievalQA.from_chain_type(llm=llm, chain_type="stuff", retriever=docsearch)
qa_chain("What is the main topic of this document?")
11. Monitoring and Logging
Implementing proper monitoring is crucial for maintaining and improving your RAG system:
import logging
from langchain.callbacks import FileCallbackHandler
logging.basicConfig(filename='rag_logs.log', level=logging.INFO)
file_handler = FileCallbackHandler("langchain.log")
llm = OpenAI(callbacks=[file_handler])
qa_chain = RetrievalQA.from_chain_type(llm=llm, chain_type="stuff", retriever=docsearch)
try:
result = qa_chain("What is the main topic of this document?")
logging.info(f"Query processed successfully. Result: {result['result']}")
except Exception as e:
logging.error(f"Error occurred: {str(e)}")
12. Handling Failures Gracefully
Here’s a simple way to handle failures:
def safe_qa(query):
try:
result = qa_chain({"query": query})
return result['result']
except Exception as e:
logging.error(f"Error processing query '{query}': {str(e)}")
return "I'm sorry, I couldn't process that query. Could you try rephrasing it?"
print(safe_qa("What is the meaning of life?"))
13. Continuous Learning and Improvement
To keep your RAG system up-to-date, implement a feedback loop:
def update_knowledge_base(query, answer, feedback):
if feedback == "correct":
new_text = f"Q: {query}\nA: {answer}"
texts.append(new_text)
docsearch.add_texts([new_text])
logging.info(f"Added new knowledge: {new_text}")
elif feedback == "incorrect":
logging.info(f"Incorrect answer logged for query: {query}")
Conclusion
By implementing these practical techniques, you can build a robust, responsive, and continually improving RAG system. The key to a successful RAG implementation lies in ongoing refinement and adaptation to your specific use case and data. Whether you’re reducing hallucinations or building smarter, data-driven AI systems, RAG is a powerful tool to explore.